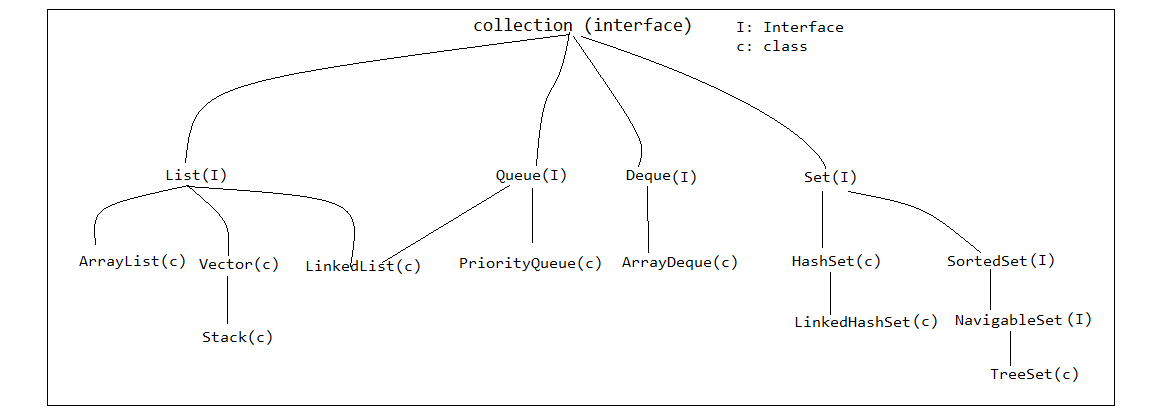

SortedSet is an interface in Java that extends Set. It maintains elements in ascending order.Comparable) or by providing a custom comparator (using Comparator).Set implementations).Methods In SortedSet
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| Comparator<? super E> comparator() | Returns the comparator used to order the elements in this set. If the set uses natural ordering, it returns null. |
| E first() | Returns the first (lowest) element currently in the sorted set. |
| E last() | Returns the last (highest) element currently in the sorted set. |
| SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements are strictly less than the specified toElement. |
| SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements are greater than or equal to the specified fromElement. |
| SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) | Returns a view of the portion of this set whose elements range from fromElement (inclusive) to toElement (exclusive). |

import java.util.SortedSet;import java.util.TreeSet;public class SortedSetExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // Using TreeSet (a class that implements SortedSet) SortedSet<Integer> sortedSet = new TreeSet<>(); // Adding elements sortedSet.add(5); sortedSet.add(1); sortedSet.add(3); sortedSet.add(10); // The elements are automatically sorted in ascending order System.out.println("Sorted Set: " + sortedSet); // Output: [1, 3, 5, 10] // Access first and last elements System.out.println("First Element: " + sortedSet.first()); // Output: 1 System.out.println("Last Element: " + sortedSet.last()); // Output: 10 // Retrieve subsets System.out.println("HeadSet (elements < 5): " + sortedSet.headSet(5)); // Output: [1, 3] System.out.println("TailSet (elements >= 3): " + sortedSet.tailSet(3)); // Output: [3, 5, 10] }}Sorted Set: [1, 3, 5, 10]
First Element: 1
Last Element: 10
HeadSet (elements < 5): [1, 3]
TailSet (elements >= 3): [3, 5, 10]NavigableSet extends SortedSet and provides additional methods to navigate through the set, allowing bidirectional navigation.Methods in NavigableSet
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| E lower(E e) | Returns the greatest element in this set strictly less than the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| E floor(E e) | Returns the greatest element in this set less than or equal to the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| E ceiling(E e) | Returns the smallest element in this set greater than or equal to the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| E higher(E e) | Returns the smallest element in this set strictly greater than the given element, or null if there is no such element. |
| E pollFirst() | Retrieves and removes the first (lowest) element, or returns null if the set is empty. |
| E pollLast() | Retrieves and removes the last (highest) element, or returns null if the set is empty. |
| NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() | Returns a view of the set in reverse order (descending order). |
| Iterator<E> descendingIterator() | Returns an iterator over the elements in this set, traversing the elements in reverse order. |
xxxxxxxxxximport java.util.NavigableSet;import java.util.TreeSet;public class NavigableSetExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // TreeSet implementing NavigableSet NavigableSet<Integer> navSet = new TreeSet<>(); // Adding elements navSet.add(10); navSet.add(20); navSet.add(30); navSet.add(40); navSet.add(50); System.out.println("Original Set: " + navSet); // Output: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] // Find nearest elements System.out.println("Ceiling(25): " + navSet.ceiling(25)); // Output: 30 (least >= 25) System.out.println("Floor(25): " + navSet.floor(25)); // Output: 20 (greatest <= 25) System.out.println("Higher(30): " + navSet.higher(30)); // Output: 40 (strictly greater than 30) System.out.println("Lower(30): " + navSet.lower(30)); // Output: 20 (strictly less than 30) // Get the set in descending order System.out.println("Descending Set: " + navSet.descendingSet()); // Output: [50, 40, 30, 20, 10] }}Original Set: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
Ceiling(25): 30
Floor(25): 20
Higher(30): 40
Lower(30): 20
Descending Set: [50, 40, 30, 20, 10]TreeSet is a concrete class that implements both NavigableSet and SortedSet.SortedSet and NavigableSet.NOTE:
TreeSet is backed by a Red-Black tree, ensuring that insertions, deletions, and lookups take O(log n) time.Comparable). Alternatively, you can pass a Comparator to TreeSet for custom sorting.SortedSet: Maintains elements in ascending order. It is the base interface that provides the ability to retrieve subsets based on range.NavigableSet: Extends SortedSet and provides advanced methods to navigate the set, such as retrieving the closest matches for a given element.TreeSet: A concrete implementation of NavigableSet and SortedSet, backed by a balanced tree, offering efficient sorting and retrieval of elements in both ascending and descending order.xxxxxxxxxximport java.util.TreeSet;public class TreeSetExample { public static void main(String[] args) { // TreeSet stores elements in sorted order TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(); // Adding elements treeSet.add("Apple"); treeSet.add("Banana"); treeSet.add("Orange"); treeSet.add("Mango"); // The elements are automatically sorted System.out.println("Sorted TreeSet: " + treeSet); // Output: [Apple, Banana, Mango, Orange] // Use methods from SortedSet and NavigableSet System.out.println("First Element: " + treeSet.first()); // Output: Apple System.out.println("Last Element: " + treeSet.last()); // Output: Orange System.out.println("Descending Set: " + treeSet.descendingSet()); // Output: [Orange, Mango, Banana, Apple] }}Sorted TreeSet: [Apple, Banana, Mango, Orange]
First Element: Apple
Last Element: Orange
Descending Set: [Orange, Mango, Banana, Apple]